Pantera™ Lux™ Coronary Drug-Coated Balloon (DCB) is indicated for balloon dilation for in-stent restenosis, de novo lesions, acute or impending vascular occlusion and treatment of small vessel disease.a

Product Highlights
Clinically proven solution
For in-stent-restenosis and further indications1-12
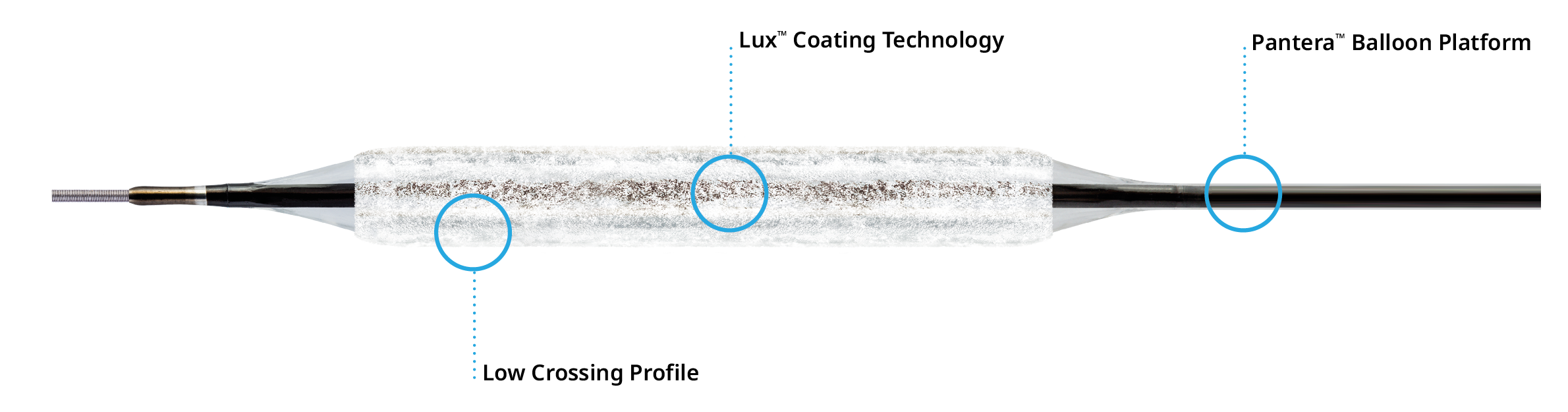
Lux™ coating technology
For rapid drug absorption13
Excellent deliverability
Lowest crossing profile for better push and easier cross14
Clinically proven solution
Clinical outcomes from multiple studies including randomized controlled trials like BIOLUX RCT, ISARDESIRE 4 and PEBSI show high efficacy and safety for both in-stent restenosis and de novo lesions.1-12
More than 3,900 patients treated in clinical studies 1-12,15-16
Pantera™ Lux™ DCB has proven efficacy and safety in multiple clinical trials investigating coronary drug-coated balloons for various implant-free treatment options.1-10

Target Lesion Failure (TLF) rate
at 18 months (p>0.99)
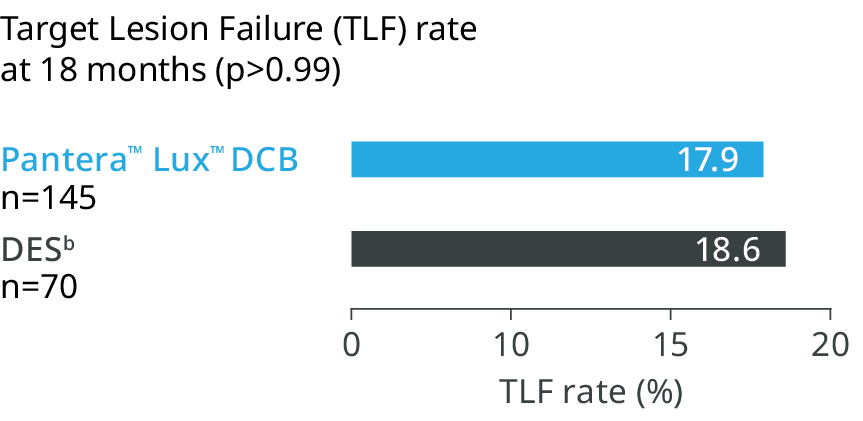
BIOLUX RCT (n=229) 4
DCB is confirmed as a viable treatment option for ISR with the advantage of avoiding an additional stent layer.
REVELATION (n=120) 8
The treatment with Pantera™ Lux™ DCB may represent a valuable alternative strategy in selected STEMI patients undergoing primary PCI.
Mean Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) rate at 9 months (p=0.27)
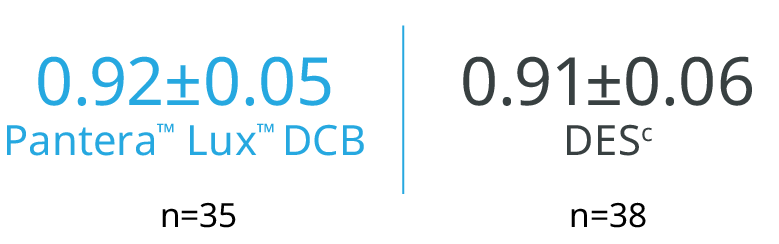
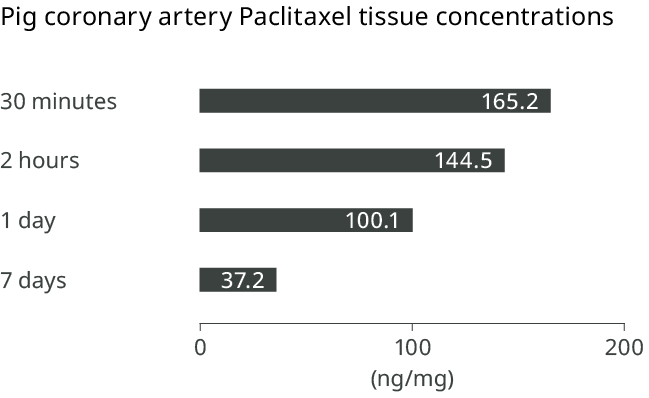
Lux™ coating technology for rapid drug absorption
The Lux™ coating technology blends paclitaxel with BTHC, a rapidly metabolized, safe and biocompatible excipient, thus improving bioavailability at the target site.13
Prolonged tissue retention at the target site
Following one application of the Pantera™ Lux™ DCB, paclitaxel can be readily detected in the treated region beyond 7 days in animal tissue.13,14
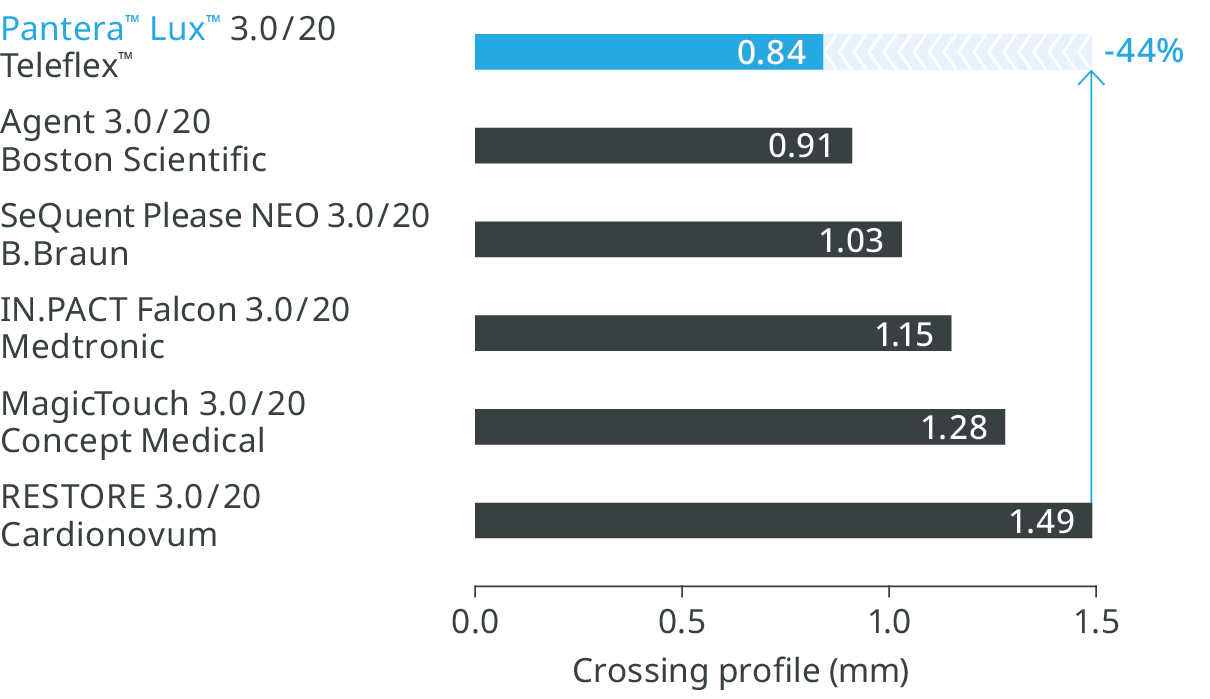
Excellent deliverability
Pantera™ Lux™ DCB, with its lowest crossing profile, provides better pushability and easier crossability.14
Lowest crossing profile14
Pantera™ Lux™ DCB has a 44% smaller crossing profile.
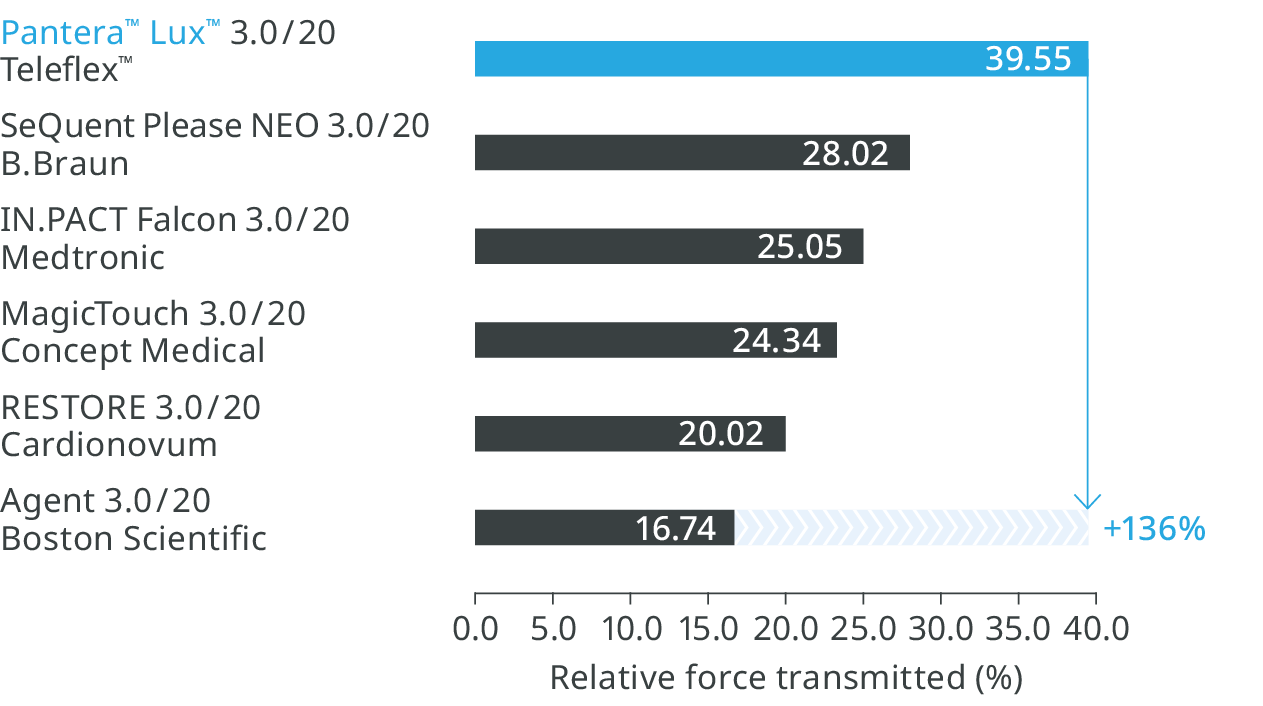
Better pushability 14
136% more force transmitted from hub to distal tip.
Best in class crossability 14
82% less force needed to cross lesions.

Clinical Highlights
BIOLUX RCT4
DCB is confirmed as a viable treatment option for ISR with the advantage of avoiding an additional stent layer
Prospective, multi-center, randomized, controlled clinical trial
See MoreREVELATION8
Excellent and comparable clinical outcome between the DCB and DES groups
24-month follow-up results from the Revelation trial comparing Pantera™ Lux™ DCB vs. 2nd generation DES in patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction
See MoreSCAAR16
Numerically lowest cumulative rate of clinically driven restenosisd
Long term outcome after treatment of de novo coronary artery lesions using three different drug-coated balloons
See MoreProduct Overview

| Drug-coated balloon catheter | |
|---|---|
| Catheter type | Fast-exchange PTCA balloon catheter |
| Recommended guide catheter | 5F (min. I.D. 0.056”) |
| Lesion entry profile | 0.017” |
| Guide wire diameter | 0.014” |
| Usable catheter length | 140 cm |
| Balloon folding | 3-fold |
| Balloon markers | Two embedded platinum-iridium markers |
| Brachial shaft marker | 92 cm from tip |
| Femoral shaft marker | 102 cm from tip |
| Proximal shaft diameter | 2.0F |
| Distal shaft diameter | 2.5F (ø 2.0 - 3.5 mm), 2.6F (ø 4.0 mm) |
| Nominal Pressure (NP) | 7 atm |
| Rated Burst Pressure (RBP) | 13 atm (ø 2.0 - 3.5 mm); 12 atm (ø 4.0 mm) |
| Coating | |
|---|---|
| Drug | Paclitaxel |
| Drug dose | 3.0 μg/mm2 |
| Coating matrix | Lux™ coating comprising Paclitaxel and Butyryl-tri-hexyl citrate (BTHC) |
| Coated area | Cylindrical section of the balloon, exceeding the proximal and distal markers |
| Balloon diameter x length (mm) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø 2.0 x 10-30 | ø 2.5 x 10-30 | ø 3.0 x 10-30 | ø 3.5 x 10-30 | ø 4.0 x 10-30 | |||||||||||
| Nominal Pressure (NP) |
atm* | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | |||||||||
| ø (mm) | 2.00 | 2.50 | 3.00 | 3.50 | 4.00 | ||||||||||
| Rated Burst Pressure (RBP) |
atm* | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 12 | |||||||||
| ø (mm) | 2.26 | 2.82 | 3.48 | 4.11 | 4.59 | ||||||||||
| *1 atm= 1.013 bar | |||||||||||||||
| Balloon | Catheter length 140 cm | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ø (mm) | Balloon length (mm) | |||||||||
| 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | ||||||
| 2.00 | 365110 | 365111 | 365112 | 365113 | 365114 | |||||
| 2.50 | 365120 | 365121 | 365122 | 365123 | 365124 | |||||
| 3.00 | 365125 | 365126 | 365127 | 365128 | 365129 | |||||
| 3.50 | 365130 | 365131 | 365132 | 365133 | 365134 | |||||
| 4.00 | 365135 | 365136 | 365137 | 365138 | 365139 | |||||